Tech Report
Recommended Mixing Equipment For Thermal Interface Materials
Application Summary
Thermal greases are viscous gels or pastes applied to electronic components to increase heat conductivity. They improve the efficiency of a heat sink by filling gaps that would otherwise hold air. Common formulations consist of ceramic or metal powders suspended in synthetic oil or grease, typically silicone.
Mixing is critical as it determines paste properties including stability, density, adhesion, consistency and spreadability. The level of dispersion and uniformity achieved in the mixing process has a direct effect on ease of application and thermal performance.
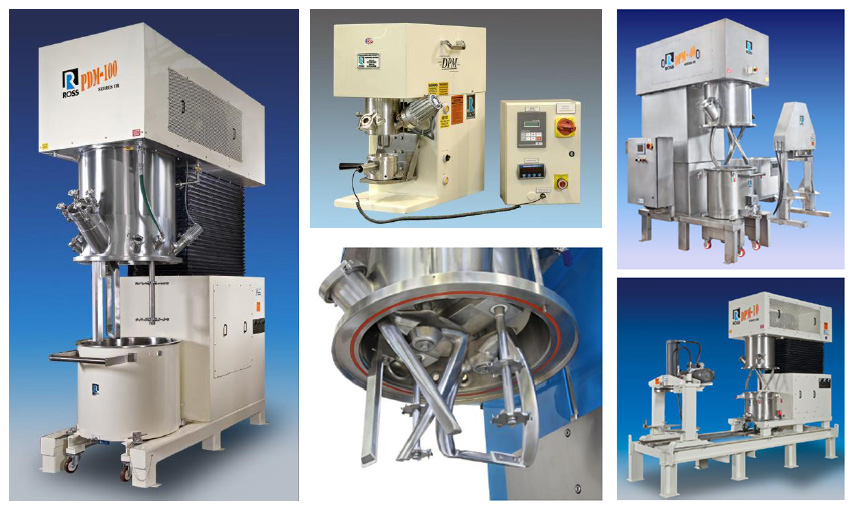
Ross Double Planetary Mixers and Planetary Dispersers
Double Planetary Mixers and Planetary Dispersers are widely used in the preparation of thermal interface materials (TIMs) which are commonly supplied in the form of viscous grease. The agitators rotate on their own axes while orbiting the vessel, imparting a very thorough mixing action even when the product is no longer free-flowing.
Though operated at relatively low speeds, a Ross Double Planetary Mixer imparts high shear and easily disintegrates agglomerates of ceramic or metal fillers in highly viscous batches up to 6 million centipoise. Lower viscosity thermal compounds benefit from high speed mixing in a Ross PowerMix Planetary Disperser which is very effective in wetting out powders and creating a fine dispersion regardless of product rheology. Other highly filled thermal pastes require two planetary stirrers and two disperser shafts for rapid incorporation of large amounts of solids into the liquid vehicle. Testing is recommended to confirm the most efficient planetary mixer design for your particular thermal grease formulation.
Other Electronic Applications typically produced in Ross Planetary Mixers:
- Battery Slurries
- Conductive Coatings
- Electrode Materials
- Epoxy Insulators
- Fuel Cell Pastes
- Solder Pastes
- Thick Film Inks
Mixing tips and benefits:
Vacuum-rated planetary mixers enable manufacturers to produce void-free gels and pastes for uniform application (via screen printing, stencil printing or syringe dispensing) and superior thermal performance. Processing under vacuum improves shearing and dispersion, helping ensure that the liquid binder encapsulates individual particles rather than agglomerates of particles. Order of raw material addition also affects the quality of the finished product and must be considered during mixer selection.
