Tech Report
Choosing the right static mixer design for viscous mixtures

Technology Brief
Static mixer designs vary widely and proper selection is key to achieving a homogenous mix within the allowed pressure drop or available pipe length. For viscous applications with space limitations but no maximum pressure drop, an Interfacial Surface Generator static mixer is recommended.
Static mixer designs
A static mixer is a device inserted into a housing or pipeline with the objective of manipulating fluid streams to divide, recombine, spread, swirl or form layers as they pass through the mixer. Mixing performance is easily predicted based on flow rate, viscosity, density, percentage of mixture components and pipe dimensions.
Different designs are available, typically consisting of plates or baffles positioned in precise angles in order to direct flow, increase turbulence and achieve mixing.
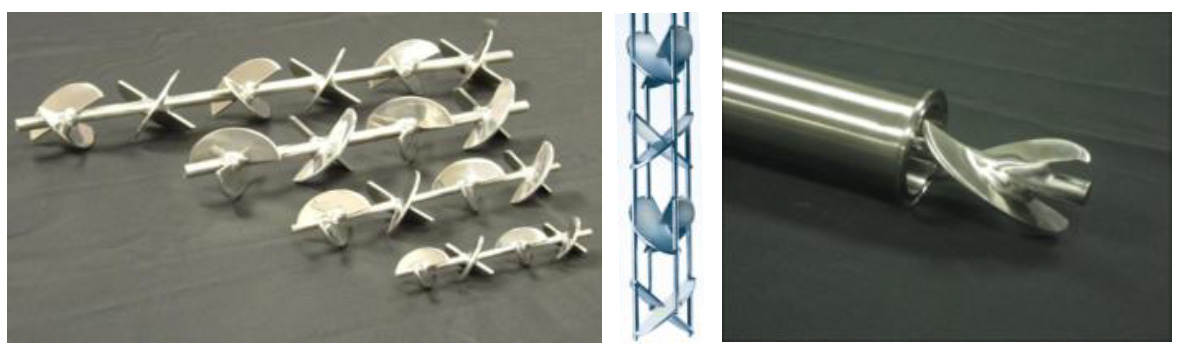
The above conventional static mixer styles are ideal for high flowrate, low viscosity applications. In such turbulent conditions, complete mixing is typically accomplished in just 4 or 6 elements with relatively minor loss in pressure. For low flow and/or high viscosity requirements, however, the number of static mixer elements of this design that is required to achieve a homogenous blend increases significantly. If the process set-up is limited in length, a move to a different style static mixer is recommended.
Interfacial Surface Generators
The Ross Interfacial Surface Generator (ISG) is a unique motionless mixer design featuring solid piece elements bored with four holes. The ends of the elements are shaped so that when stacked together, adjacent elements form a tetrahedral chamber. If two input streams enter the ISG static mixer, the number of layers emerging from the first, second and third elements are 8, 32 and 128. This exponential progression generates over two million layers in just 10 elements.
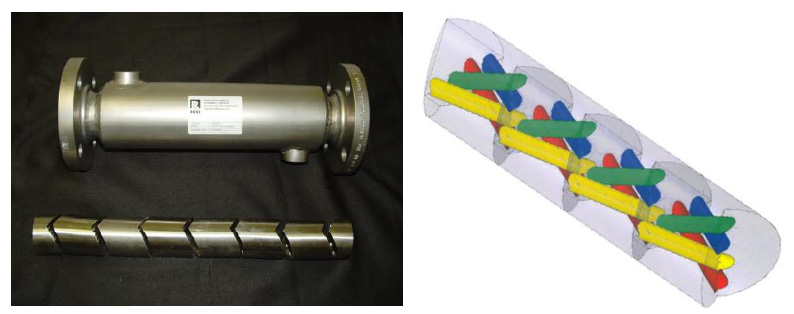
The ISG`s mixing mechanism is ideal for high viscosity and laminar flow applications with a Reynolds number below 500. Blending a minor component such as a low-viscosity dye, catalyst or additive into a viscous fluid is a classic ISG application. This mixer can handle a wide range of products, from foods to polymers, to adhesives, plastics and composites. The ISG is also suitable for sanitary processes since the elements are easily removed from the housing to be cleaned and sanitized individually.
Due to the geometry of the ISG elements, complete mixing is achieved in a very short length of pipe so this type of static mixer is also utilized for turbulent flow requirements with space limitations and no maximum pressure drop.
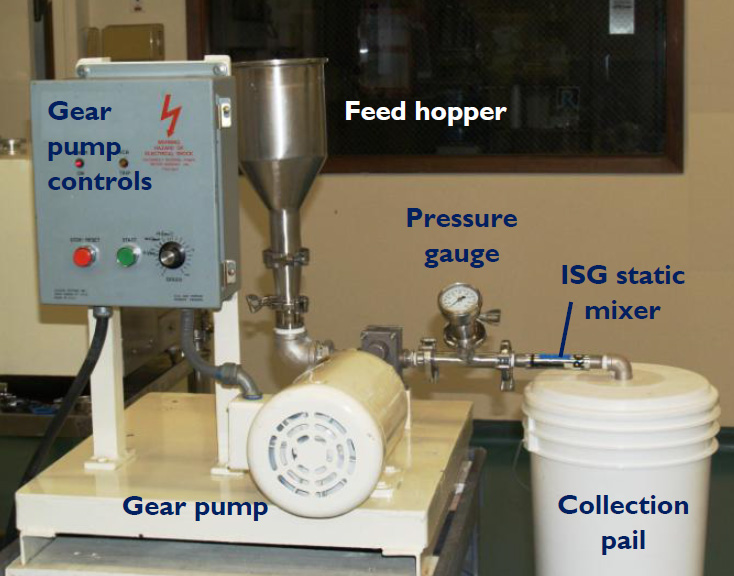

Sample Application: Oil-in-Water Gel Emulsion
Pilot-scale trials were performed to determine how well the Ross ISG Static Mixer can reduce droplet size for a particular viscous gel emulsion. Target droplet size: <5 microns.
The base emulsion consisting of 98% aqueous gel and 2% oil was prepared using a batch-style pitched blade mixer. This material was very shear-thinning -- 121,000 cP at 0.5 rpm spindle speed and only 31,400 cP at 3 rpm. A gear pump was used to force the product through the ISG mixer. In a single pass at 4.75 gpm, median droplet size dropped from 19.46 to 4.07 microns. In another run, the base emulsion was fed at a slightly higher flowrate, 6.6 gpm, and the resulting droplet size after one pass was 2.56 microns.